Cervical Treatment in Aurangabad
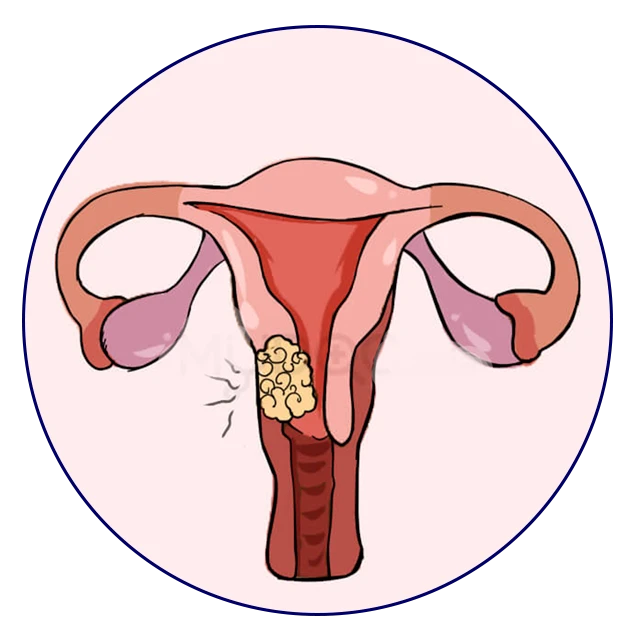
Cervical cancer
The cervix’s cells give rise to the cancerous development known as cervical disease. The cervix is located in the lower, thin end of the uterus (belly). The cervix connects the uterus and vagina (birth trench). Malignant cervical development typically advances gradually over time. Before the cervix develops malignant growth, the cells undergo changes known as dysplasia, during which abnormal cells first appear in the cervical tissue. The abnormal cells may eventually transform into disease cells, start to grow, and spread even more deeply into the cervix and surrounding areas if they are not destroyed or eradicated.
Overview
When exposed to HPV, the body’s immune system typically prevents the virus from doing harm. In a small percentage of people, however, the virus survives for years, contributing to the process that causes some cervical cells to become cancer cells. You can reduce your risk of developing cervical cancer by having screening tests and receiving a vaccine that protects against HPV infection.
Symptoms
Early-stage cervical cancer generally produces no signs or symptoms.
Signs and symptoms of more-advanced cervical cancer include:
- Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between periods or after menopause
- Watery, bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and have a foul odor
- Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse
Squamous cell carcinoma: Squamous cell carcinomas make up to 90% of cervical malignancies. These malignancies originate in the ectocervix’s cells.
Adenocarcinoma:
Cervical adenocarcinomas foster in the epithelial cells of the endocervix. Clear-cell adenocarcinoma, called clear-cell carcinoma or mesonephroma, is an uncommon sort of cervical adenocarcinoma.
Since HPV is communicated physically, HPV immunization offers the most security when given before an individual becomes physically dynamic. The individuals who are now physically active might get less advantage from the antibody. This is because physically passionate individuals might have been presented with some of the HPV types designated by the immunization. The Habitats for Infectious prevention and Counteraction suggests routine HPV vaccination for young ladies and men at age 11 or 12, and the series can begin at age nine. For youngsters who weren’t inoculated inside the age proposals, HPV immunization is prescribed up to mature 26 years. A few grown-ups between the ages of 27 and 45 who are not currently inoculated may choose to get HPV immunization after talking with their PCP about their gamble of new HPV diseases. Youngsters who start the immunization series before age 15 need two dosages to be safeguarded. The individuals who accept their most memorable portion at age 15 or more seasoned need three dosages to be secured. Dive more deeply into HPV antibodies and how they safeguard against cervical disease and different kinds of malignant growth.
